Integrate JupyterHub
The following steps describe how to deploy a fully integrated JupyterHub server. When JupyterHub is deployed, data scientists can create and share Jupyter notebooks.
Procedure
-
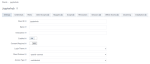
Log in to the master console of the Access Manager, using the dcadmin user at https://hostname/auth/admin/master/console, where “hostname” is the hostname/IP of the VM where the platform is installed.
-
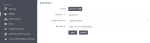
Go to Clients and click Create.
-
Set jupyterhub as the Client ID.
-
Set https://hostname/jupyter as the Root URL.
-
Click Save.
-
Connect to the VM where the platform is installed, and then connect to the Postgres container:
Copykubectl exec -it postgres-67fc4f87f8-vwvsf shNote: The postgres container has a different name in each case, but it always starts with ‘postgres’. While entering the command, after typing ‘post’, press the Tab key to autocomplete the container name.
-
Connect to the PostgreSQL server:
Copypsql -U postgres -
Execute the following SQL statements:
CopyCREATE ROLE jupyter_user LOGIN PASSWORD 'jupyter_password';
ALTER USER jupyter_user WITH CREATEDB;
CREATE DATABASE jupyter_db;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE jupyter_db TO jupyter_user; -
Close the PostgreSQL connection, and then exit the container:
Copy\qCopyexit
-
Use snap to install Helm:
Copysudo snap install helm –classicNote: For more details regarding the installation of Helm, see https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/. If you don’t have snap installed, see Install snap and https://snapcraft.io/docs/installing-snapd.
-
Add the JupyterHub repository to Helm:
Copyhelm repo add jupyterhub https://jupyterhub.github.io/helm-chart/Copyhelm repo update
-
Replace <RANDOM_HEX> with a randomly generated HEX string. You can run the following command in the terminal to generate the string:
Copyopenssl rand -hex 32 -
Replace <PLATFORM_ADDRESS> with the hostname/IP of the machine running the platform.
-
Replace <TENANT> with the tenant name from Access Manager, where you initially created the jupyterhub client.
-
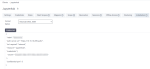
Replace <CLIENT_SECRET> with the value of the secret from the jupyterhub client, initially created in Access Manager. The secret is included in the JSON file that you have downloaded.
-
Replace <DB_PASSWORD> with the password for the jupyter_user, created earlier in the PostgreSQL server.
In these instructions, we used jupyter_password.
-
Use Helm to install JupyterHub using the config.yaml file that you edited earlier:
Copyhelm upgrade --cleanup-on-fail --install jupyter jupyterhub/jupyterhub --namespace jupyter --create-namespace --version=0.10.3 --values config.yaml -
Apply the ingress.yaml file to Kubernetes:
Copykubectl apply -f ingress.yaml -
Access JupyterHub at https://hostname/jupyter, where “hostname” is the hostname/IP of the VM where the platform is installed.
Wait for the JupyterHub to start.

Comments
0 comments