Manage data and data sources in a dataset (Step 2)
When creating or editing a dataset, you can manage the data sources and their columns as needed.
Prerequisites
- You are creating or editing a dataset.
- The Step 2 – Refine page is open.
Procedure
You can manage the data sources as follows:
Click  Add more data and follow the required steps for adding a new data source or a new connection. See also the following topics:
Add more data and follow the required steps for adding a new data source or a new connection. See also the following topics:
Click a connection or a file, and then click  next to its name.
next to its name.
Important: Deletion is performed without confirmation and cannot be undone. You can readd the connection by clicking  Add more data.
Add more data.
The following options are available:
Rename – Click
 rename data source and specify a new name for the data source.
rename data source and specify a new name for the data source. The data sources (tables) names within the dataset must be unique.
Remove – Click
 remove next to the name of the data source.
remove next to the name of the data source. Readd a data source – Click the arrow next to the connection name, and then select the data source.
You have several options for adding a calculation to a dataset. For details, see About calculations.
Add a filter to reduce the amount of data available for analysis in a dataset. The resulting dataset and all the visualizations based on it will contain only data that are already filtered. In addition, visualizations will run faster. For details, see Add filters.
If no security filters are added, it means that all the data in a shared dataset is visible to all its recipients. With a security filter, some recipients have access only to a subset of data that is relevant to them. For example, each department can see the data related to the respective department and not the whole dataset. For details, see Row-level security filters.
You can manage the columns of each data source as follows:
The following options are available:
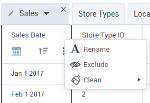
Rename – Click
 column options, and then click Rename. Edit the name as needed.
column options, and then click Rename. Edit the name as needed.Exclude – Point to the column, click
 column options, and then click Exclude.
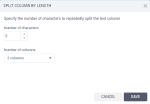
column options, and then click Exclude.Split – Point to the column, click
 column options, and then click one of the following options:
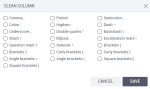
column options, and then click one of the following options:Clean – Point to the column, click
 column options, and then click one of the following options:
column options, and then click one of the following options:Format
- Make uppercase – Make all characters uppercase.
- Make lowercase – Make all characters lowercase.
- Capitalize first letter – Make the first letter uppercase and turn the rest to lowercase.
Remove
Punctuation – Remove selected types of punctuation in a string column.
NULLs – Add a filter to remove all rows with the NULL value in a column.
Blanks – Add a filter to remove all blank rows in a string column.
Zero values – Add a filter to remove all rows with zero value in a numeric column.
Negative values – Add a filter to remove all rows with a negative value in a numeric column.
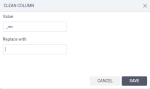
Replace
Trim
Leading & Trailing spaces – Remove spaces at the beginning and at the end of the string in a column.
Leading spaces – Remove spaces at the beginning of the string in a column.
Trailing spaces – Remove spaces at the end of the string in a column.
All spaces – Remove all spaces in a column.
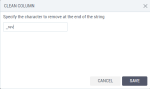
Leading character – Remove the specified character at the beginning of the string, in a column.
Trailing character – Remove the specified character at the end of the string, in a column.
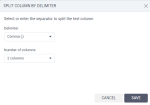
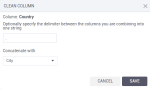
Concatenate – Join two strings into one, with or without a separator in between.
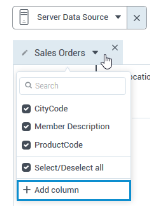
Readd – Click the arrow next to the name of the data source. Then, select the column that you want to readd.
Sort alphabetically – Point to the column, and then click
 sort column.
sort column.Add new column – (Server data sources only) Click the arrow next to the name of the data source. Then, click the Add column and select the columns in the Add column dialog.
For each data source, check if the data roles are identified correctly. To adjust them, see Change the data role.
Check the aggregation type for the columns. Adjust the aggregation if needed. The aggregation type that is defined at the time of a dataset creation is a default type for that measure in a visualization.
For details, see Change the data aggregation.
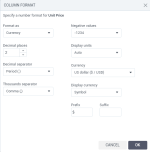
In the Column format dialog, select the format type to apply, customize its options, and click OK.
You can customize the following format options:
Decimal places
- Select the number of decimal places to display in the number. For example, depending on the decimal places, a number may look like 3.14 or 3.14159.
Decimal separator
- Select the separator to show for decimals: Comma (,), Period (.), Space (), or Custom to provide another separator symbol.
Thousands separator
- Select which separator to show every thousand, for example, 10,000 or 10.000.
- You can select Comma (,), Period (.), Space (), or Custom to provide another separator symbol. To show the number without any separator, select Custom and leave the field empty.
Negative values
- Select how to display negative values: -1234, (1234), or 1234-.
Display units
- Select a specific unit to abbreviate the numbers: None, Auto, Thousands (K), Millions (M), Billions (B), Billions (G), and Trillions (T).
- For example, if the number is 47,000 and the display units are Thousands (K), the number is shown as 47K.
Prefix
- Specify characters that precede each displayed number.
Suffix
- Specify characters that follow each displayed number.
You can customize the following format options:
Decimal places
- Select the number of decimal places to display in the number. For example, depending on the decimal places, a number may look like 3.14 or 3.14159.
Decimal separator
- Select the separator to show for decimals: Comma (,), Period (.), Space (), or Custom to provide another separator symbol.
Thousands separator
- Select which separator to show every thousand, for example, 10,000 or 10.000.
- You can select Comma (,), Period (.), Space (), or Custom to provide another separator symbol. To show the number without any separator, select Custom and leave the field empty.
Negative values
- Select how to display negative values: -1234, (1234), or 1234-.
Display units
- Select a specific unit to abbreviate the numbers: None, Auto, Thousands (K), Millions (M), Billions (B), Billions (G), and Trillions (T).
- For example, if the number is 47,000 and the display units are Thousands (K), the number is shown as 47K.
Currency
- Select a currency from the list or specify the custom currency.
Display currency
Select how to display currency: as a symbol ($) or as an international symbol (USD).
Prefix
- Specify characters that precede each displayed number.
Suffix
- Specify characters that follow each displayed number.
You can customize the following format options:
Decimal places
- Select the number of decimal places to display in the number. For example, depending on the decimal places, a number may look like 3.14 or 3.14159.
Multiply by 100
- Select whether to multiply the number representing a percentage. For example, the value of 0.05 will be formatted as 5%.
Comments
0 comments